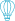
he Gobi Desert is commonly cited as the sixth largest desert in the world by area. It spans across northern China and southern Mongolia, covering an area of approximately 1,295,000 square kilometers (500,000 square miles). It's notable for its diverse landscapes, including sand dunes, Rocky Mountains, gravel plains, salt flats, and occasional oases. The Gobi Desert plays a significant role in shaping the climate and ecology of the region, and it has been an important historical and cultural region for millennia.
The climate of the Mongolian Gobi Desert is characterized by low precipitation, high evaporation rates, and harsh weather conditions. Summers are hot, with temperatures often exceeding 40°C (104°F), while winters are cold, with temperatures dropping below freezing. The region experiences occasional sandstorms, particularly during the spring months. Water is scarce in the Gobi Desert, with limited surface water sources such as intermittent streams and oases. Underground water reserves, accessed through wells, are essential for human and animal survival in the region.